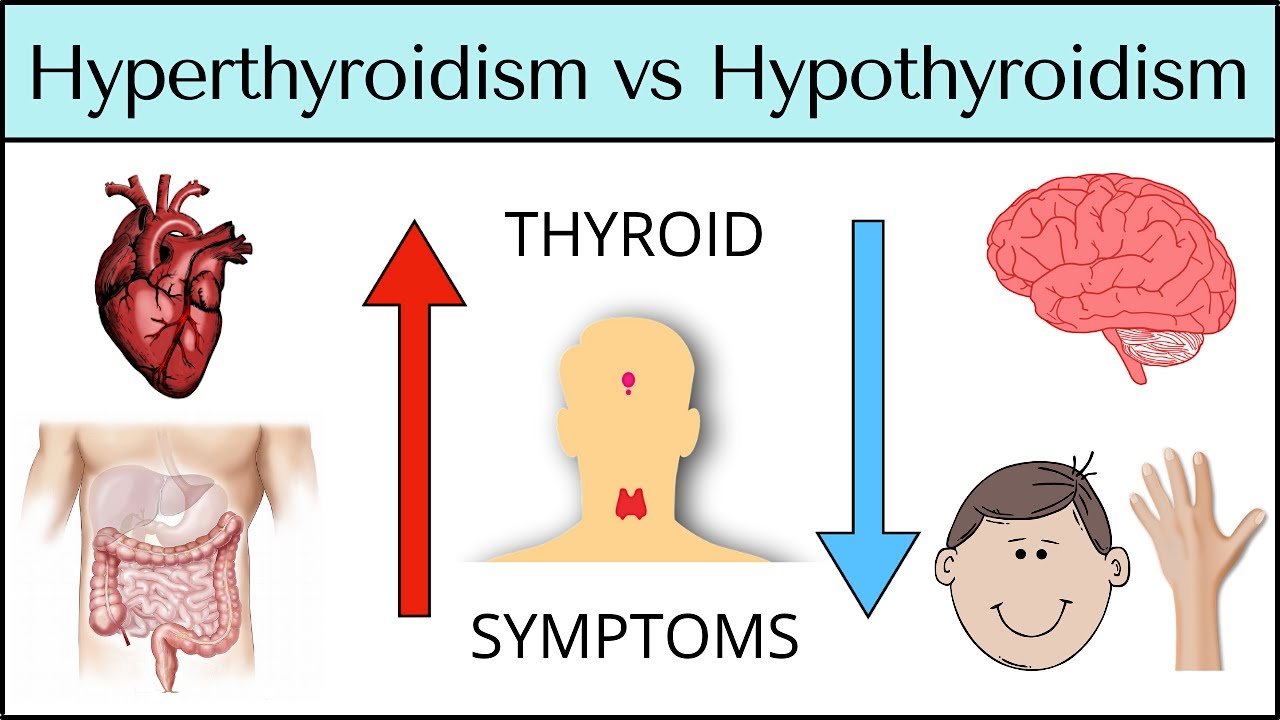
Your thyroid plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, energy, and hormones. But when it’s out of balance, it can lead to serious health issues. Many women struggle with thyroid imbalance, experiencing fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and more. But is it hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism? Understanding the differences between an underactive vs. overactive thyroid can help you get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Hypothyroidism vs. Hyperthyroidism: The Basics
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid): The thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones, slowing down metabolism.
- Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid): The thyroid produces too many hormones, speeding up metabolism.
Symptoms: How to Spot the Differences
Hypothyroidism vs Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
| Symptom | Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid) | Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Levels | Fatigue, sluggishness | Restlessness, anxiety |
| Weight Changes | Weight gain despite diet | Unexplained weight loss |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Feels cold often | Always feeling warm, sweating |
| Heart Rate | Slow heartbeat | Rapid or irregular heartbeat |
| Hair & Skin | Thinning hair, dry skin | Hair loss, thin skin |
| Mood Changes | Depression, brain fog | Nervousness, irritability |
| Menstrual Cycle | Heavy, irregular periods | Light or absent periods |
Causes of Thyroid Disorders
Hyperthyroidism vs Hypothyroidism Causes
- Hypothyroidism: Hashimoto’s disease (autoimmune), iodine deficiency, or thyroid removal.
- Hyperthyroidism: Graves’ disease (autoimmune), thyroid nodules, or excess iodine.
Diagnosis: How to Test for Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism vs Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis
Doctors use thyroid function tests to check hormone levels:
- TSH test: High TSH suggests hypothyroidism; low TSH suggests hyperthyroidism.
- T3 & T4 tests: Measures thyroid hormone levels in women.
- Antibody tests: Detect autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease.
Treatment Options
Hyperthyroidism vs Hypothyroidism Treatment
- Hypothyroidism: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy (levothyroxine).
- Hyperthyroidism: Medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery to reduce thyroid activity.
Thyroid Medication Side Effects
- Hypothyroidism meds: Can cause palpitations, insomnia if dosage is too high.
- Hyperthyroidism meds: May lead to liver issues, fatigue, or allergic reactions.
How Thyroid Disorders Affect Women’s Health
Thyroid Issues and Menstrual Cycle
- Hypothyroidism: Can cause heavy or irregular periods.
- Hyperthyroidism: Often leads to light or absent periods.
Thyroid Disorders and Weight Gain
- Hypothyroidism slows metabolism, leading to weight gain.
- Hyperthyroidism speeds up metabolism, causing weight loss.
Thyroid Problems and Hair Loss
- Both conditions can trigger thinning hair or hair shedding due to hormonal imbalances.
Managing Thyroid Disorders Naturally
Natural Remedies for Thyroid Imbalance
- Reduce stress with meditation and yoga.
- Get enough sleep to support hormone balance.
- Limit processed foods and sugar intake.
Thyroid Health Diet for Women
- For hypothyroidism: Eat iodine-rich foods (seaweed, dairy), selenium (Brazil nuts), and zinc (pumpkin seeds).
- For hyperthyroidism: Avoid excess iodine (seafood, iodized salt) and caffeine.

Final Thoughts
Thyroid health is essential for women’s well-being. Recognizing the signs of thyroid problems in females can help you take action early. Whether you’re dealing with weight changes, fatigue, or menstrual irregularities, getting the right tests and treatment is key. If you suspect a thyroid issue, consult a doctor to discuss thyroid function tests and treatment options.