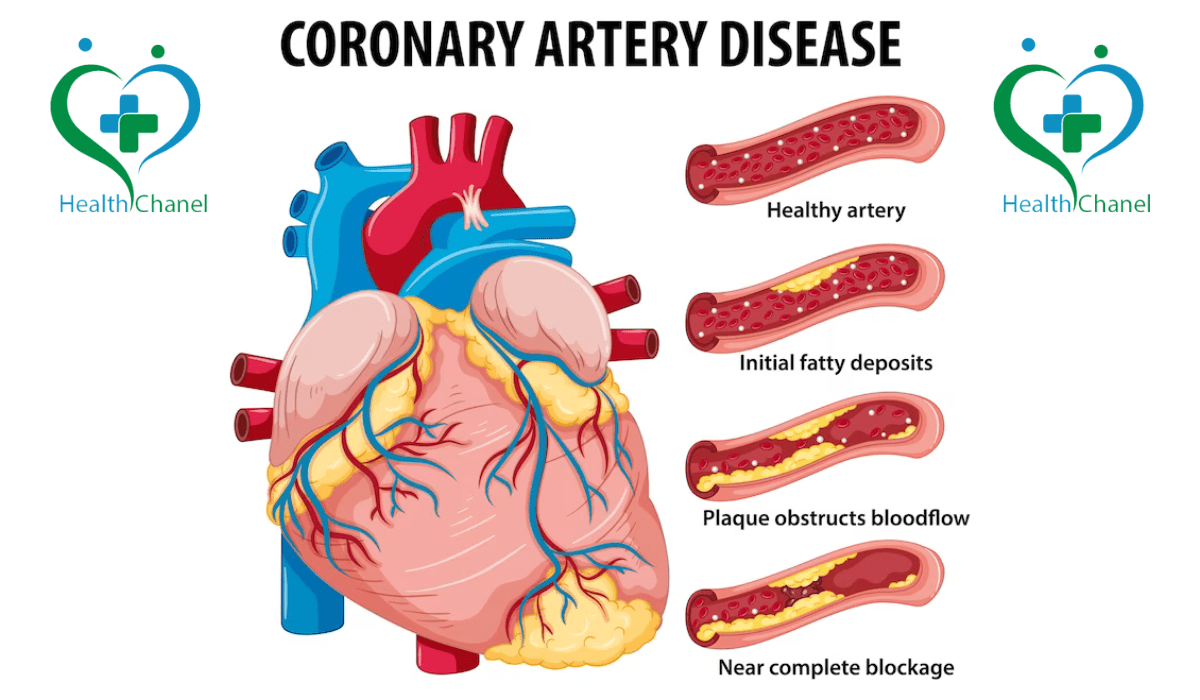
Heart disease remains one of the biggest health concerns worldwide, and CAD disease (Coronary Artery Disease) is one of the most common forms. It develops gradually due to plaque in arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attacks. Many people don’t recognize the signs of blocked arteries until the condition becomes severe. Understanding CAD symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments can help you take proactive steps toward better heart health and prevention.
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
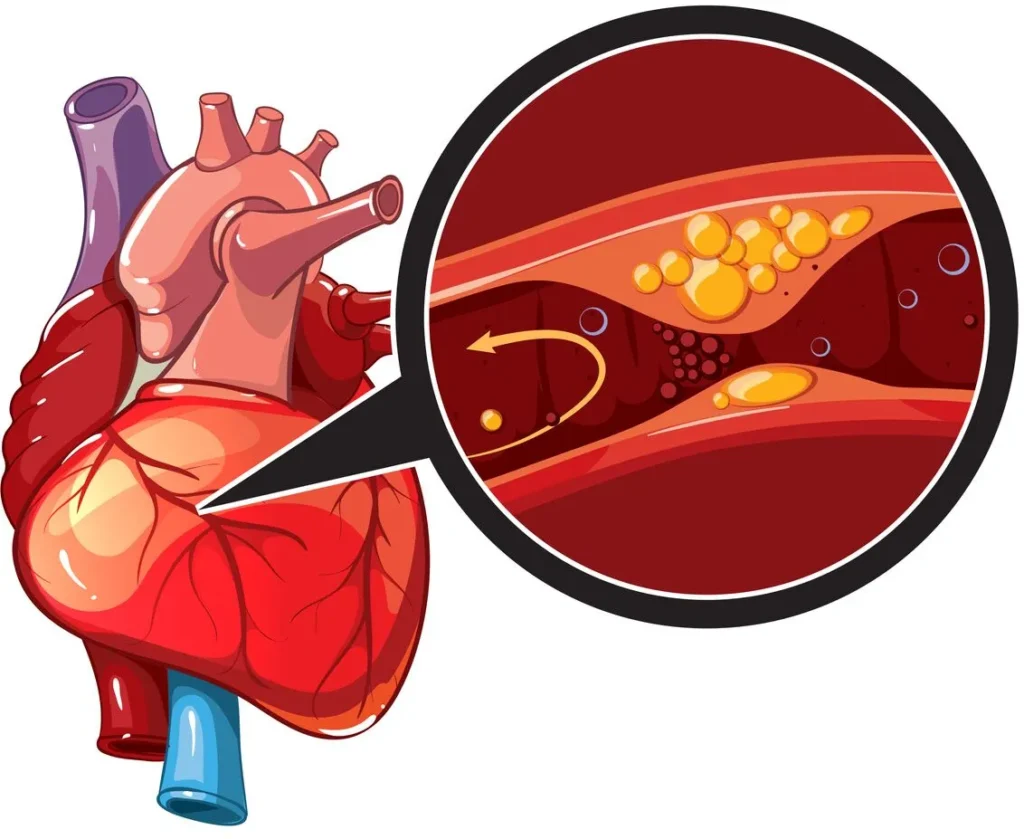
Atherosclerotic disease, or CAD disease, occurs when fatty deposits build up inside the arteries, leading to clogged arteries and reduced oxygen supply to the heart. Over time, this process—known as hardening of the arteries—can lead to severe complications like heart attacks, arrhythmias, and heart failure.
According to the atherosclerosis definition, this condition is caused by plaque buildup in the arteries due to cholesterol, fat, and other substances. It is a leading cardiovascular disease cause and a major contributor to arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), a type of cardiac disease that affects blood circulation.
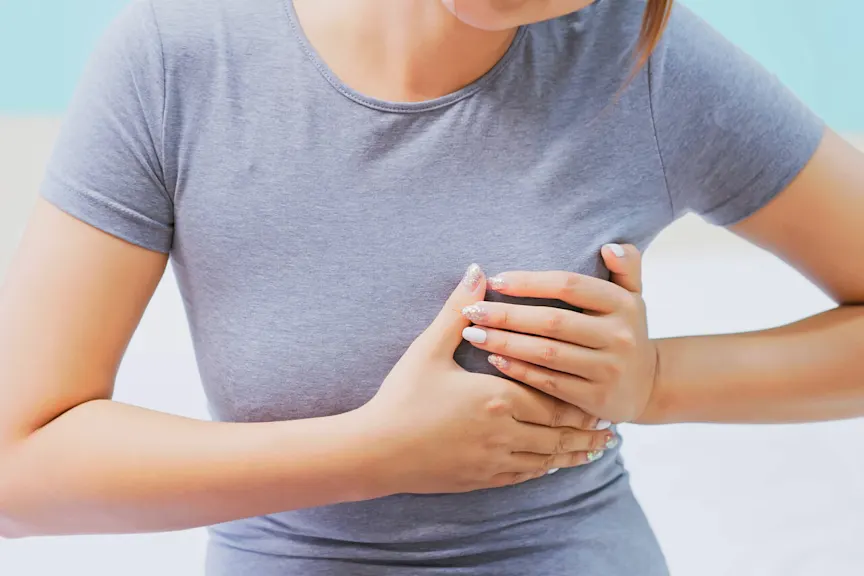
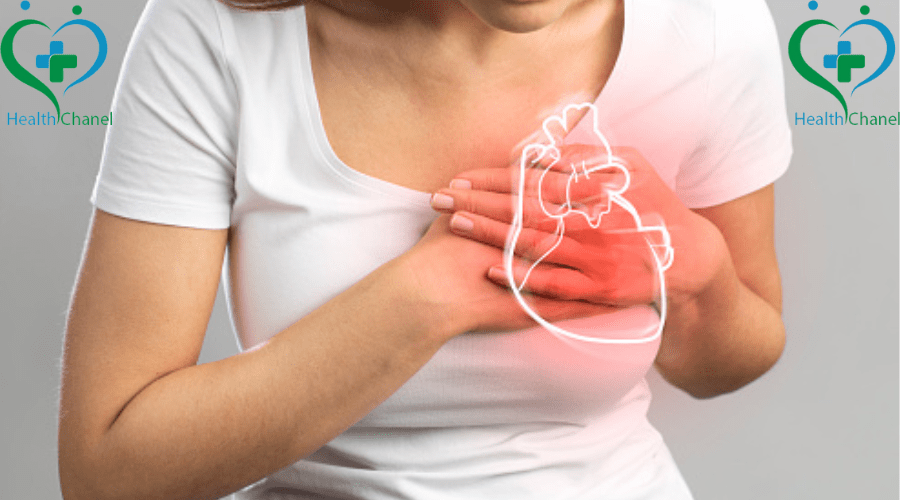
Common CAD Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
CAD symptoms may not be noticeable in the early stages, but as plaque in arteries increases, they become more apparent. Some key symptoms of hardening of the arteries include:
- Chest pain (angina) – A feeling of tightness, pressure, or discomfort, especially during exertion.
- Shortness of breath – Difficulty breathing, particularly with physical activity.
- Fatigue – Unexplained exhaustion due to reduced oxygen supply to the heart.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness – A sign that your heart isn’t getting enough blood.
- Pain in the arms, neck, jaw, or back – This may indicate a heart issue, especially in women.
If you notice signs of minor heart blockage, such as occasional chest pain or fatigue, consult a doctor for a cardiovascular risk assessment to prevent complications.
Cardiovascular Disease Causes and Risk Factors
Several CVD risk factors contribute to the development of atherosclerotic disease:
- High cholesterol – Leads to plaque in arteries and blockages.
- High blood pressure – Damages artery walls, making them more prone to blockages.
- Diabetes – Increases the risk of atherosclerosis symptoms.
- Smoking – Speeds up the process of hardening of the arteries.
- Obesity and poor diet – Contribute to high cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Sedentary lifestyle – Lack of exercise weakens heart function.
- Family history – Genetics play a role in developing cardiac disease.
Diagnosis and Atherosclerosis Treatment
Early atherosclerosis diagnosis is essential for effective management. Doctors may use tests like coronary angiography, CT scans, or stress tests to check for signs of blocked arteries. Once diagnosed, a treatment for CAD plan may include:
- Lifestyle changes – A heart-healthy diet, exercise, and quitting smoking.
- Medications – Medicine for heart patients includes cholesterol-lowering drugs, blood thinners, and beta-blockers.
- Surgical procedures – In severe cases, angioplasty, stents, or bypass surgery may be necessary.
The ACC AHA guidelines emphasize early detection and intervention to prevent complications. Following these recommendations can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: How to Protect Your Heart
Taking steps toward cardiovascular disease prevention can reduce your risk of CAD disease:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet – Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise regularly – Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity most days.
- Manage stress – Practice mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
- Monitor your numbers – Keep track of cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol – Both contribute to clogged arteries.
- Regular check-ups – A cardiovascular risk assessment can help detect issues early.
Conclusion
CAD disease is a serious but preventable condition. By recognizing atherosclerosis symptoms early and following the ACC AHA guidelines, you can improve your heart health and lower your risk of cardiac disease. Whether you have signs of minor heart blockage or advanced atherosclerotic disease, taking proactive steps today can lead to a healthier future. If you experience any signs of blocked arteries, seek medical help immediately—your heart deserves it!
To read related articles, Click here