Hair loss can feel overwhelming, but understanding its root cause is the key to finding a solution. Did you know that deficiencies in vitamins like B12 and D are common culprits? These essential nutrients play a vital role in maintaining healthy hair, and their absence can lead to thinning, shedding, and even bald patches. The good news? Hair loss caused by vitamin deficiencies is often reversible with the right steps. Let’s explore, ”Which vitamin deficiency causes hair loss?”
Which Vitamin Deficiency Causes Hair Loss?
When it comes to hair health, deficiencies in essential vitamins like B12 and D are common culprits. These deficiencies disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, leading to thinning, shedding, and even bald patches. Let’s explore the role of each vitamin in maintaining healthy hair.
Vitamin B12 and Hair Loss
You might wonder, “Can B12 deficiency cause hair loss?” The answer is yes! Vitamin B12 is vital for red blood cell production, which ensures your hair follicles get the oxygen and nutrients they need to thrive. Without enough B12, your hair becomes weaker, leading to thinning and shedding.
B12 Deficiency Hair Loss Symptoms:
- Increased hair shedding or brittleness.
- Fatigue, which may indicate your body isn’t producing enough healthy red blood cells.
- Slower hair regrowth, even after shedding stops.
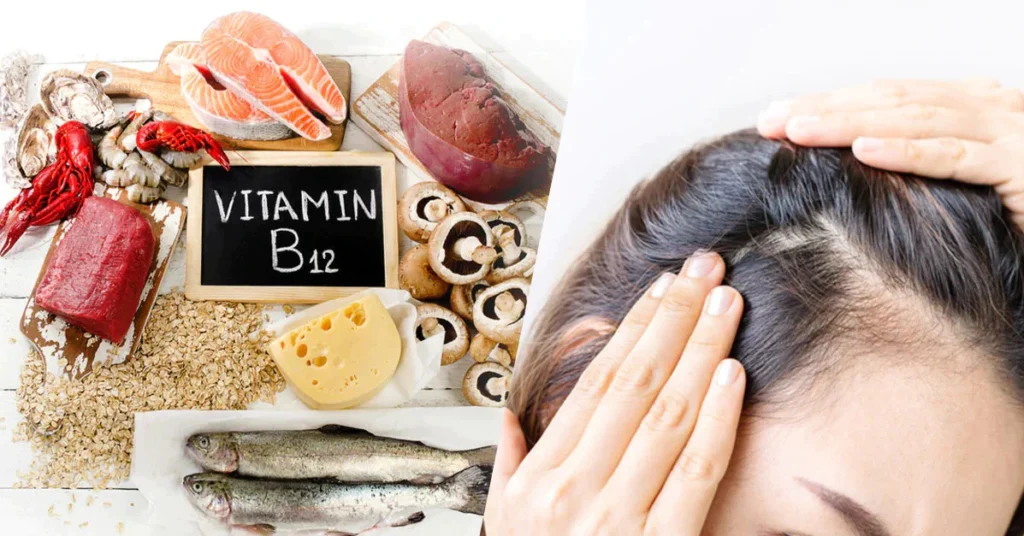

How to Address B12 Deficiency:
- Add foods like eggs, fish, and dairy to your diet.
- Consider taking a B12 supplement for hair shedding, especially if you’re vegan or vegetarian, as plant-based diets often lack this vitamin.
The good news? With the right diet and supplementation, you can reverse hair loss caused by a B12 deficiency and encourage healthy hair growth.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss
Vitamin D is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” but lacking Vitamin D can lead to significant hair loss. This essential vitamin plays a role in stimulating hair follicles and supporting the hair growth cycle.
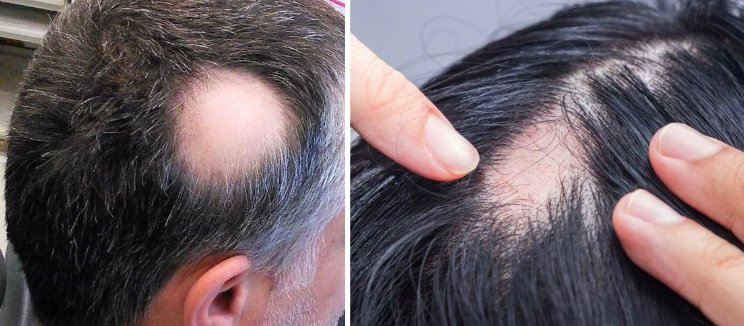
Is Vitamin D Hair Loss Reversible?
Yes, it is! If caught early, increasing your Vitamin D levels through diet, sunlight, or Vitamin D supplements for hair loss can promote regrowth and prevent further shedding.
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms:
- Thinning hair or bald patches.
- Weak, brittle strands prone to breakage.
- Other symptoms like fatigue, bone pain, or muscle weakness.
Best Vitamin D Sources:
- Natural sunlight exposure.
- Foods like salmon, fortified milk, and egg yolks.
- A high-quality Vitamin D supplement for hair growth.
If you’re wondering about the connection between Vitamin D and hair loss due to a poor diet, the solution lies in consistent intake. Whether through supplements or diet, replenishing your Vitamin D levels can restore hair health.
Other Nutritional Deficiencies That Cause Hair Loss
Hair health relies on a variety of nutrients, and deficiencies in the following vitamins and minerals can contribute to thinning or shedding:
- Iron Deficiency: Often linked to hair shedding in females, iron supports healthy blood flow to the scalp. Consider a test to see what vitamins you need if hair loss is persistent.
- Zinc and Biotin: These nutrients are staples in many vitamins for hair growth and thickness. A lack of these can disrupt the hair growth cycle.
- Protein Deficiency: Hair is made of keratin, a protein, so a poor diet low in protein can weaken strands.
How to Identify Vitamin Deficiency Symptoms for Hair Loss
The first step to solving hair loss is identifying its cause. You can take specific steps to pinpoint whether a nutritional deficiency that causes hair loss is behind your shedding:
- Consult a doctor to perform blood tests for B12, Vitamin D, iron, and other essential nutrients.
- Look for common symptoms, such as brittle hair, fatigue, or slowed regrowth.
This proactive approach can help determine whether you’re dealing with alopecia vitamin deficiency or another condition, ensuring targeted treatment.
Best Supplements for Hair Loss
Supplements can bridge the gap when your diet isn’t enough. Here are some recommendations:
- Vitamin D Supplements for Hair Loss: Ideal for those with limited sun exposure.
- B12 Supplements for Hair Shedding: Vital for hair regrowth and overall follicle health.
- Multivitamins for Hair Growth and Thickness: Containing biotin, zinc, and iron for comprehensive hair care.
For females experiencing hair loss, choose supplements for hair loss in females tailored to hormonal or nutritional imbalances.
Will Hair Loss Due to Poor Diet Grow Back?
Yes, hair loss caused by poor diet and nutritional deficiencies is often reversible with the right interventions. By correcting the deficiency and providing your hair with the nutrients it needs, you can promote regrowth. Incorporating a healthy, balanced diet alongside targeted supplements for hair growth and thickness is key.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss can feel overwhelming, but understanding its root cause—whether it’s B12 deficiency hair loss, lacking Vitamin D, or another deficiency— empowers you to take action. By addressing deficiencies that cause hair loss and incorporating the best supplements for hair shedding, you can restore your hair’s health and vitality.
Remember, your hair is a reflection of your overall health. If you suspect a vitamin deficiency, consult with a healthcare professional to perform tests and develop a personalized plan. With the right care and attention, hair loss and nutritional deficiency don’t have to hold you back—healthy, luscious hair can be yours again!
Also Read
7 Ways to Regrow Hair Naturally in 3 Weeks: Proven Tips for Thicker, Healthier Hair Fast
Hair Loss During Shower: How Much is Too Much?



